Logical Group Instruction Set of 8085 Microprocessor | ANA, ANI, ORA, ORI, XRA, XRI, CMA, CMC, STC, CMP, RLC, RAL, RRC, RAR instruction examples
Logical Group
These Logical group instructions are used in the 8085 Microprocessor program. In this article, you would get the instructions with example. In some sections, referring images are also provided to make your understanding crystal clear.
- ANA r
- Here the data of r AND (Logical AND) with the data of Accumulator and the result will store in Accumulator.
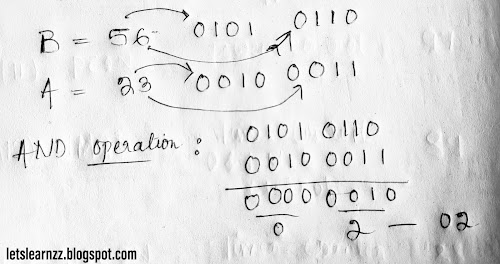
(B) ⋀ (A) ⟶ (A)
Data in Accumulator is 23 and data in register B is 56.
After executing the program,
Data in Accumulator will be 02
(Can't Understand Refer This Image )
- ANA M
- Here the data in the memory location pointed by HL pair AND (Logical AND) with data in Accumulator and the result will store in Accumulator.
((H-L)) ⋀ (A) ⟶ (A)
Data in Accumulator is 23 and data in ((H-L)) is 56
After executing the program,
Data in Accumulator will be 02.
- ANI data
- Here the data AND with the value of Accumulator and the result will store in Accumulator.
(56) ⋀ (A) ⟶ (A)
Data in Accumulator is 23
After executing the program,
Data in Accumulator will be 02.
- ORA r
- Here the data in entered register OR with the value of Accumulator and the result will store in Accumulator.
(B) ⋁ (A) ⟶ (A)
Data in register 'B' is 56
Data in Accumulator is 23
After Execution of Program,
Data in Accumulator will be 77
(Can't understand refer this image)
- ORA M
- Here the data in the memory location pointed by HL pair OR with the value of Accumulator and the result will store in Accumulator.
((H-L)) ⋁ (A) ⟶ (A)
Data in ((H-L)) is 56
Data in Accumulator is 23
After execution of the program,
Data in Accumulator will be 77.
- ORI data
- Here the entered data OR with the data of Accumulator and the result will store in Accumulator.
(05) ⋁ (A) ⟶ (A)
Data entered is 05
Data in Accumulator is 45
After execution of the program,
Data in Accumulator will be 45.
- XRA r
- Here the data in entered register X-OR with the data in Accumulator and the result will store in Accumulator.
(B) ∀ (A) ⟶ (A)
- XRA M
- Here the data in the memory location pointed by HL pair X-OR with the data in the accumulator and the result will store in the accumulator.
((H-L)) ∀ (A) ⟶ (A)
- XRI data
- Here the entered data X-OR with the data in Accumulator and the result will store in the accumulator.
(05) ∀ (A) ⟶ (A)
- CMA
- This instruction means to complement the data in the accumulator.
Data in Accumulator is 56 (0101 0110)
After Execution of the program,
Data in the accumulator will be 1010 1001 (A9)
- CMC
- This instruction is used to complement the content in carry.
- STC
- This instruction is used to set the value of carry.
- CMP r
- Here a comparison action will happen between the content of register and accumulator. Flag bit changes.
- CMP M
- Here a comparison action will happen between the content of memory location pointed by HL pair and the content of accumulator.
- CPI data
- Here a comparison action will happen between the mentioned data and the contents of the accumulator. The Sign flag will get affected.
- RLC
- Means: Rotate Accumulator Left.
- Here the content of An ⇢ An+1, A7 ⇢A0 and A7 ⇢ CS
- RAL
- Means: Rotate Accumulator through Carry
- Here the content of An ⇢ An+1, A7 ⇢ CS and CS ⇢ A0
- RRC
- Means: Rotate Accumulator Right
- Here the content of A0 ⇢ A7, A0 ⇢ CS and An+1 ⇢ An
- RAR
- Means: Rotate Accumulator Right through Carry.
- Here the content of A0 ⇢CS, CS ⇢ A7 and An+1 ⇢ An
Comments
Post a Comment